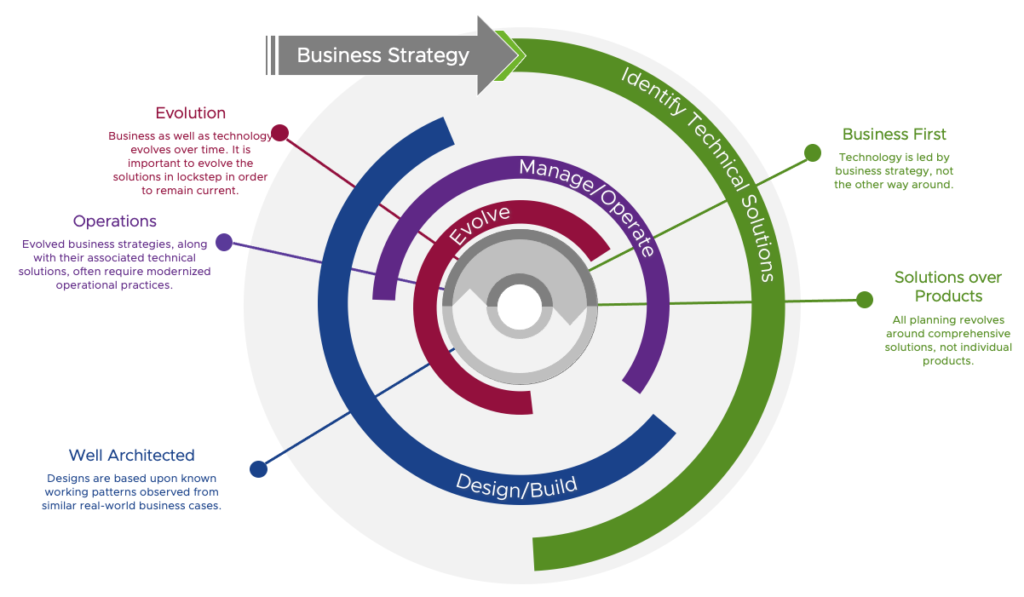
We can summarize this approach into a 3-step recurring cycle that aligns with significant changes to overall business strategies within an organization.
- Review and define current business goals.
- Identify technical solutions that address the business goals, design/build the final solution, and adjust operations to manage the implementation.
- Evolve the solution as needed per minor changes to business goals.
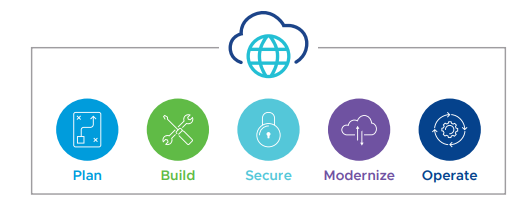
VMware Cloud Ready Framework (VMCRF) builds upon the following VMware pillars — Plan, Build, Secure, Modernize, and Operate. These pillars will help customers execute against their multi-cloud strategy, and will help organizations build reliable, scalable, secure, and operationally efficient cloud environments
VMware Cloud Ready Framework pillars
Multi-cloud concepts
Organizations must decide on a cloud strategy that meets the needs of their business, whether that is hybrid cloud and/or multi-cloud. Hybrid cloud is defined as the use of private cloud, and public cloud platforms to provide a flexible mix of cloud computing services, allowing for consistent infrastructure, simplified workload migration and placement. Multi-cloud, by comparison, is defined as the use of
two or more public cloud providers with or without any existing private cloud infrastructure. Multi-cloud is an emerging strategy employed by organizations that need to meet specific technical requirements and business outcomes by leveraging services across multiple cloud providers simultaneously. Organizations adopt this approach when faced with a scenario where no one cloud platform is able to meet all their technical requirements or deliver all the necessary outcomes for the business. This often occurs through mergers and acquisitions (M&A), where businesses find themselves with application, operational and financial ownership across clouds that may not align with their initial cloud strategy. This model affords organizations the flexibility, choice, and unique opportunity to be intentional about their approach to infrastructure and application modernization (e.g., refactor/build, replatform, rehost/migrate, retain, or retire).
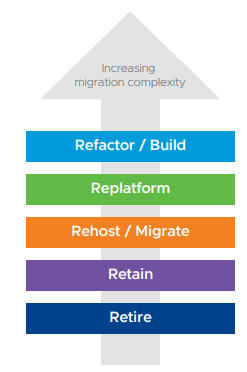
• Refactor / Build involves changing the application at the source code level. Typically, applications are re-written to take advantage of cloud microservices architecture and to incorporate new services such as IoT, machine learning, and others.
• Replatform involves changing the operating system, such as going from Windows to Linux, modifying the application middleware, such as going from a self-managed database to a cloud provider-managed database or from a virtual machine to a container image.
• Rehost / Migrate involves either changing the hypervisor. (e.g., migrate applications from one virtualized environment to another) which is known as Rehost or moving an application without changing the underlying hypervisor or application at a source code level (e.g., migrate VMs from one virtualized environment to another without requiring changes) which is known as Relocate.
• Retain means leaving workloads in a private cloud environment
• Retire means decommissioning workloads and/or converting to SaaS.
VMware Cloud Tech Zone site, including additional structured content built upon the three constructs mentioned above. We have already started the process with content targeting the Disaster Recovery use case. Other use cases will be available from the “Use Cases” drop-down menu at the top navigation bar of Tech Zone.