Zone-redundant storage replicates your data across three storage clusters in a region. Each cluster is physically separated from the other two, which means that each cluster is supplied by separate utilities, such as power or networking.
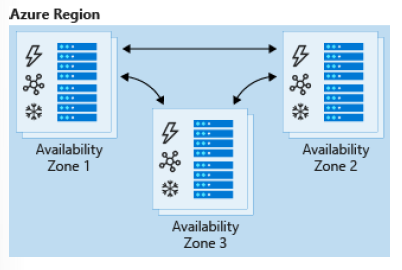
If there’s an outage in a datacenter, you can still access your data from another availability zone in that region. Data is normally replicated to two or three availability zones, depending on the region. An availability zone (AZ) is a physical location that’s made up of one or more datacenters in a region. There are typically two or three AZs per region, where each AZ is independent of the other AZs in the region.
ZRS offers 99.9999999999 percent durability of data. However, ZRS might not protect you from a regional outage, because all AZs reside in the same region. To migrate data to ZRS from either LRS or GRS requires some planning and manual migration. And it requires a tool such as AZCopy.
Limitations
ZRS for managed disks have the following restrictions:
- Only supported with premium solid-state drives (SSD) and standard SSDs.
- Currently available only in the West US 2, West Europe, North Europe, and France Central regions.
- Can’t currently be used with Azure Backup or Azure Site Recovery.
Using Azure Portal Create a VM with ZRS OS disk
- Login in to the Azure portal.
- Navigate to Virtual machines and follow the VM creation.
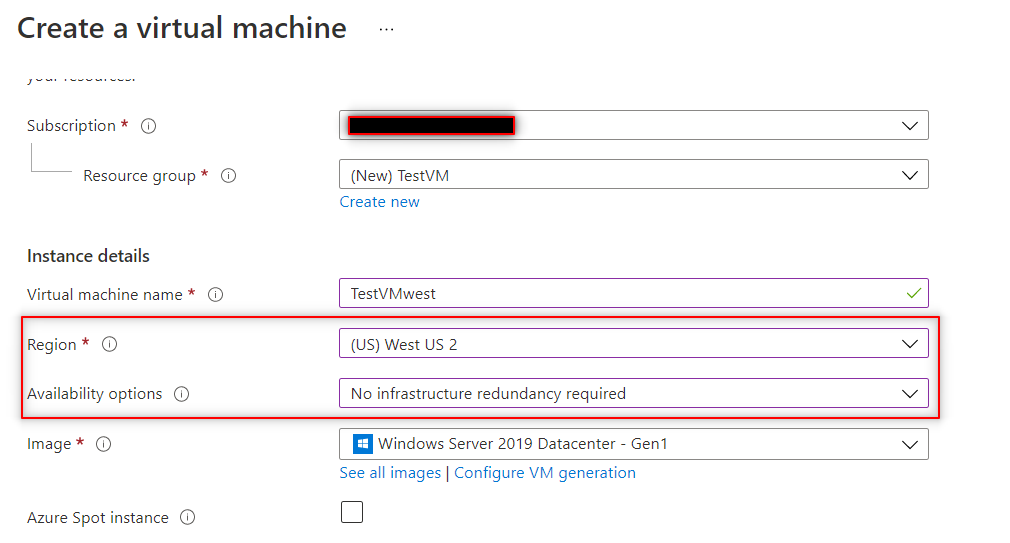
- Select a region and set Availability options to No infrastructure redundancy required.
- Proceed to the Disks pane.
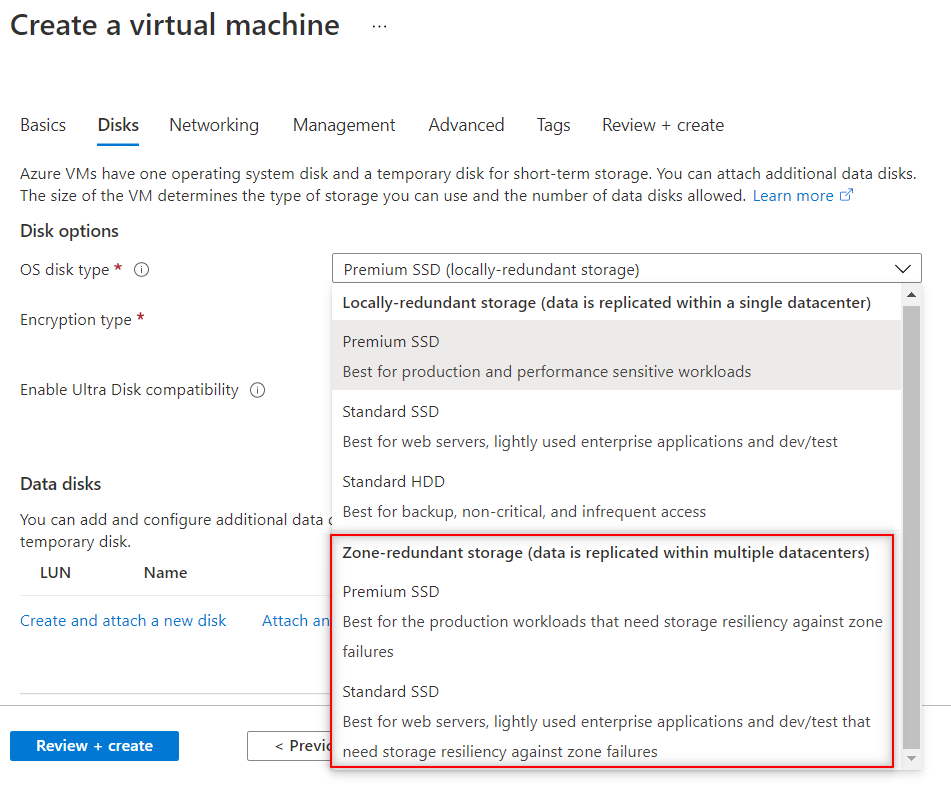
- Select OS disk type and select one of the ZRS disks in the drop down.
- Proceed through the VM deployment.
You’ve now deployed a VM with a ZRS OS disk.
For more details- Deploy a managed disk that uses zone-redundant storage